Linux Fundamentals
A brief overview of the fundamentals of Linux.
Linux Fundamentals
We will be covering the following topics:
- Linux File System
- Changing Directories
- Display Contents of a Directory
- Creating and Editing Files Using Vi
- Modifying Files
- Creating Folders
- User and Permission Management
- Networking Basics in Linux
- Package Management and Software Installation
Linux File System
There are THREE different “root” terms in Linux.
- The root user – This is the administrator account.
- The root filesystem – This is the / of the filesystem hierarchy. Think of this as C:> in Windows.
- The root home folder – This is the home folder of the root user, located in the root of the filesystem. It is located at /root.
Logging in as root > logging in as the admin account
Going into the root of the system > /
Going into the root home folder, or ~ as root > /root.
This structure helps users and applications access files systematically. Common directories include:
- /bin (binary executables)
- /etc (configuration files)
- /home (user home directories)
- /var (variable data like logs)
Another representation of the Linux file system:
/
├── bin - Essential binaries (e.g., ls, cp)
├── boot - Bootloader files (e.g., kernel, initramfs)
├── dev - Device files (e.g., /dev/sda)
├── etc - System configuration files
├── home - User home directories
│ ├── user1
│ └── user2
├── lib - Shared libraries for essential binaries
├── media - Mount points for removable media
│ ├── usb
│ └── dvd
├── mnt - Temporary mount points
├── opt - Optional software packages
├── proc - Kernel and process information (virtual filesystem)
├── root - Home directory for the root user
├── run - Runtime data for processes
├── sbin - System binaries (e.g., reboot, fdisk)
├── srv - Data for services (e.g., web server files)
├── sys - Kernel and hardware information (virtual filesystem)
├── tmp - Temporary files (cleared on reboot)
├── usr - User programs and data
│ ├── bin - User binaries
│ ├── lib - Shared libraries for user binaries
│ ├── share - Shared resources (e.g., man pages)
│ └── local - Locally installed software
└── var - Variable files (e.g., logs, cache, spool)
├── log - Log files
├── cache - Application caches
└── spool - Queued tasks (e.g., mail, printing)
Changing Directories
Using the file system from above, if you were in /var/log and wanted to navigate to /home/user1:
- cd /home/user1
- This is an absolute path.
- cd ../../home/user1
- This is a relative path.
- cd .. > cd .. > cd home > cd user1
Others include:
- cd ~
- This will take you to your home directory.
- /home/username if USER, /root if ROOT
- cd ~username
- This will take you to the home directory of the user specified.
Display Contents of a Directory
- ls
- This will show the contents of the directory you are in.
- ls -la
- This will show more information about the files, like ownership, permissions, hidden files, and size.
- -l shows detailed information, -a shows all files (including hidden files)
- tree
- This shows a more graphical view of the files and folders.
- To install, run the command:
- sudo dnf -y install tree
Creating and Editing Files Using Vi
Navigate to the directory the file is to be created in.
- touch filename.txt
- This will create a blank file.
- Can also open Vi and create a new file at the same time: vi newfile.txt
- vi filename.txt
- Hit the "i" key to enter INSERT mode.
- Edit the file as necessary.
- Hit the "esc" key to escape.
- To save and quit:
- :wq to write the file to disk (saves), and quits
- :q! to force Vi to quit without saving
Modifying Files
- mv originalFile.txt renamedFile.txt
- This will rename a file.
- cp firstFolder/file secondFolder/file
- This will copy a file from one folder to another.
- Using a WildCard Character:
- cp firstFolder/file secondFolder/file
- For example, (*.txt) matches all files with a .txt extension, and (file *) matches any file starting with file.
- rm file
- This will remove/delete a file.
Creating Folders
- mkdir newFolder
- mkdir newFolder/subFolder
- Creates a folder within a folder
- mkdir -p newFolder/subFolder
- Creates both folders at once
To remove a folder:
- rm -d folder
A folder must be empty prior to removing the folder. To remove files inside of the folder:
- rm folder/*
BRUTE FORCE DELETION:
- rm -rf folder
- -r for recursive - go through all the files and folders under this folder and wipe it all out
- -f for force - do not prompt for verification
- DO NOT RUN THIS COMMAND: sudo rm -rf /
- This will delete every file, folder, and device from your Linux machine. This rm command deletes everything starting in the root file system.
User and Permission Management
Add a user:
- sudo adduser username
Specify a name to the user:
- *sudo useradd username -c "Person Name"
Verify user:
- cat /etc/passwd
- This lists the account, name, UID, GUI, and shell for each user
Specify the password for user:
- sudo passwd username
Create a group:
- sudo groupadd groupName
Add user to a group:
- sudo usermod username -aG groupName
The commands chmod, change mode, and chown, change owner, are used to change permissions on a file or folder:
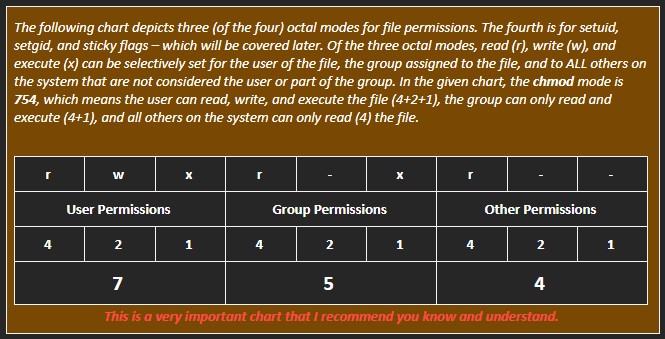
Networking Basics in Linux
Use ipconfig or ip addr to display the system's network configuration.
Test network connectivity to a website, like google.com, using the ping command.
Download files using the command line:
- curl URL
- Client URL
- Used to send and receive data
- Supports different protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP
- wget URL
- Web Get
- Used only for downloading files
- Supports different protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP
Package Management and Software Installation
- sudo dnf update
- This updates the list of packages (software) available to install or update.
- sudo dnf upgrade
- This will upgrade any out of date packages on your system to the latest version.
Installing software:
- sudo apt install software OR sudo dnf install software
- This installs the software on your system.
- sudo systemctl enable software
- This enables the software.
- sudo systemctl start software
- This starts the software.
- sudo systemctl status software
- This can help verify that the service has started and is running.